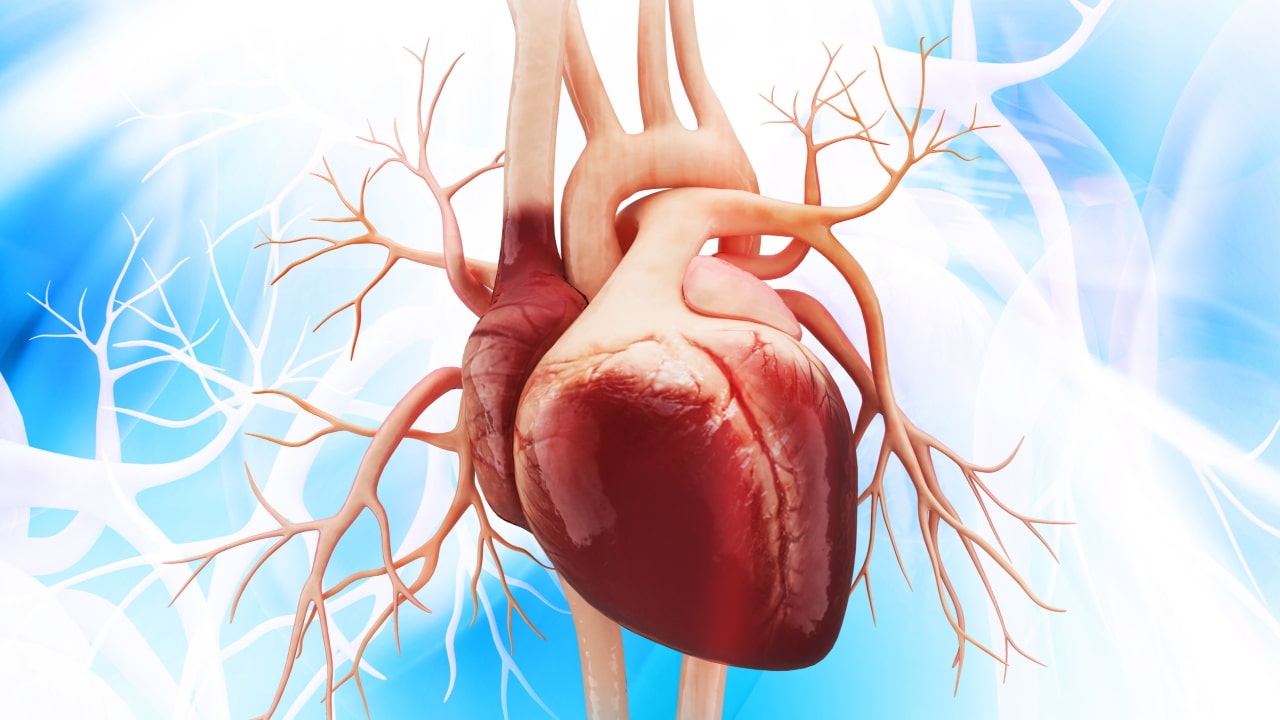
Angina
Viewing Study Tools Requires a Membership
55% of NURSING.com users are visual learners, and 35% stop using their textbooks altogether.
Angina, characterized by chest pain due to inadequate blood flow to the heart muscle, is commonly caused by coronary artery disease (CAD). Other causes include anemia, heart failure, stress, overexertion, and abnormal heart rhythms. The primary goal in managing angina is to restore adequate blood flow to the heart, evidenced by decreased chest pain and improved activity tolerance. Nursing interventions include EKG monitoring to detect arrhythmias, administering the MONA protocol (Morphine, Oxygen, Nitroglycerin, Aspirin) for acute coronary syndrome, drawing cardiac enzymes to assess myocardial damage, monitoring blood pressure, and providing cluster care to allow for rest and reduce myocardial oxygen demand.
This nursing cheatsheet will help you learn about Angina and the essential nursing interventions for effective management.