
Hemodynamic Values
Add your email below to Create your
FREE Account
![]()
Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log in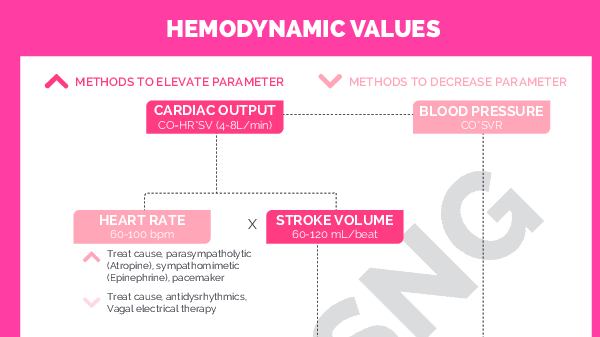

Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log in





![]()

Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log inWhat Others Say About Learning Hemodynamic Values With NURSING.com
. . . and a few more reviews.
Hemodynamic Lab Values
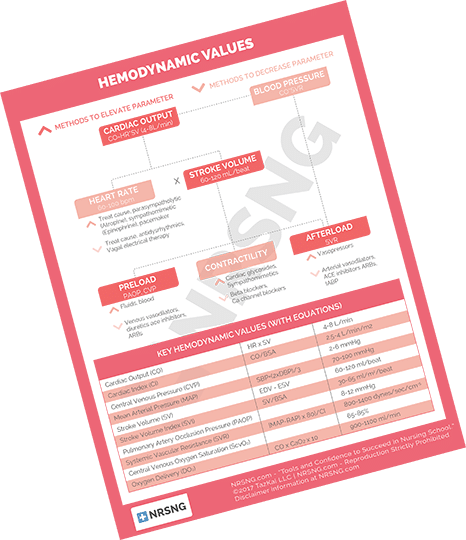
Hemodynamics refers to the study of blood flow and the forces involved in the circulation of blood within the cardiovascular system. Hemodynamic lab values are measurements that provide information about the functioning of the cardiovascular system. These values are crucial for assessing the health of the heart and blood vessels. Here are some key hemodynamic lab values:
Blood Pressure:
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP): The pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts.
Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP): The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): The average pressure in the arteries during a cardiac cycle.
Cardiac Output (CO):
Cardiac Output: The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. It is calculated as the product of heart rate (beats per minute) and stroke volume (the amount of blood ejected with each heartbeat).
Stroke Volume (SV):
Stroke Volume: The amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction.
Heart Rate (HR):
Heart Rate: The number of heartbeats per minute.
Central Venous Pressure (CVP):
Central Venous Pressure: The pressure in the vena cava, near the right atrium of the heart. It reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump blood into the arterial system.
Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR):
Systemic Vascular Resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the systemic circulation. It reflects the tone of the arterioles and the ease with which blood can flow through the systemic circulation.
Pulmonary Arterial Pressure (PAP):
Pulmonary Arterial Pressure: The pressure in the pulmonary artery. It is important for assessing the functioning of the right side of the heart and the pulmonary circulation.
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP):
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure: Also known as pulmonary artery occlusion pressure, it is an indirect measure of left atrial pressure and is often used as an estimate of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure.
These values are obtained through various diagnostic procedures, such as blood pressure measurement, echocardiography, and invasive monitoring techniques. Hemodynamic monitoring is particularly important in critical care settings, such as intensive care units (ICUs), to assess and manage patients with cardiovascular conditions. Interpretation of these values requires a comprehensive understanding of the cardiovascular system and the patient’s clinical context.
Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log inDon't forget to claim your FREE Cheatsheet

Do you know all of the standard Hemodynamics Values?
This cheatsheet makes it easy to remember.
Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log inGet Your Free Copy of "63 NCLEX Labs" Today!
"Would suggest to all nursing students . . . Guaranteed to ease the stress!"
~Jordan

Create Your Free Account
Unlock FREE access to nursing videos to pass your tests and improve your grades
Sign up with
Already have an account?
Log in