Watch More! Unlock the full videos with a FREE trial
Included In This Lesson
Study Tools
Access More! View the full outline and transcript with a FREE trial
Example Nursing Diagnosis for Cholecystitis
- Acute Pain: Cholecystitis often causes severe abdominal pain. This diagnosis addresses the pain management needs of the patient.
- Risk for Infection: Cholecystitis can lead to infection or abscess formation. This diagnosis emphasizes infection prevention.
- Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements: Cholecystitis may affect the patient's ability to tolerate and digest food. This diagnosis addresses nutritional deficits.
Transcript
So, in this Cholecystitis care plan, we're going to talk about the desired outcome of our patient, the subjective and objective data, along with the nursing interventions and rationale for each SAR, medical diagnosis is Cholecystitis.
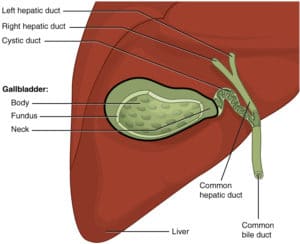
So, Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, which holds bile that is actually released into the small intestines. So, let's imagine this is our small intestines here. So, when that bile duct between the gallbladder and the small intestines gets blocked, the bile becomes trapped causing that inflammation in the gallbladder. The obstruction of the bile duct causes inflammation and it could be caused by gallstones, biliary, sludge infections, tumors, or blood vessel compression. So, the desired outcome of our patient is that they'll be free from pain and resume and maintain optimal diet and nutrition.
Now, let's look at our care plan. So, the patient may be experiencing some nausea and loss of appetite because of the blockage that isn't allowing the bile to flow into the intestines. So, the patient may be experiencing severe abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant or in the center because of the blockage and inflammation.
Now, let's look at our objective data. So, the inflammation of the gallbladder might cause your patient to have a fever. Your patient may begin vomiting due to the blockage of the bile. The patient may have abnormal lab values like their liver enzymes because the liver is what creates the bile that then travels through the bile duct into the gallbladder. So, when Cholecystitis progresses and the tissue begins to die, the liver becomes more affected resulting in those elevated liver enzymes and even sometimes jaundice. So, Bilirubin may be elevated indicating bile duct obstruction as well. The patient might have clay colored stool because of the lack of bile to change the color of the stool to brown.
Now, let's look at our nursing interventions in the rationales. So, our first nursing intervention is to assess your patient's vital signs. Look for tachycardia and fevers, because that could indicate infection in your patient. Next, you will assess the gastrointestinal status of your patient. Look for abdominal distension, listen for belching and feel for abdominal rigidity.
Our next nursing intervention is to assess and manage your patient's pain. The inflammation and obstruction causes pain that might radiate to the back. Next, you administer medications for the patient, such as antibiotics for infections, analgesics for pain, antiemetics for nausea and vomiting, and IV fluids to help hydrate your patient while they're resting their bowels. Be sure to monitor the diagnostic testing of your patient. Look at those lab values in the imaging to view the gallbladder and how it's doing. So, you will prepare for any procedures that they might have. The patient might be on a clear liquid diet prior, and you will have to withhold any anticoagulants and NSAIDS to avoid bleeding.
Our last nursing intervention is to provide nutrition and lifestyle education, encourage a low fat diet because it's easier to digest and avoid gastric irritants because they could worsen diarrhea. The diarrhea after gallbladder removal occurs because of the direct drainage of the bile into the intestine from the liver. It no longer will have the gallbladder to rest in. It's going to go straight into the intestines causing diarrhea.
We love you guys. Now go out and be your best self today and as always, happy nursing!
View the FULL Transcript
When you start a FREE trial you gain access to the full outline as well as:
- SIMCLEX (NCLEX Simulator)
- 6,500+ Practice NCLEX Questions
- 2,000+ HD Videos
- 300+ Nursing Cheatsheets
“Would suggest to all nursing students . . . Guaranteed to ease the stress!”