Nursing care for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) is focused on managing the underlying pathology and promoting heart health. CAD occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, leading to narrowed arterial passages and impaired blood flow to the heart. As nurses, our primary goal is to assess, prevent, and manage CAD effectively.
Assessment plays a pivotal role in nursing care for CAD patients. Nurses should be vigilant in recognizing the signs and symptoms of CAD, such as chest pain, arrhythmias, shortness of breath, and elevated blood pressure. Electrocardiograms (EKGs), cholesterol levels, CT scans, angiograms, and stress tests are essential diagnostic tools ordered by physicians to evaluate the extent of vessel occlusion and stenosis. Through comprehensive assessment, nurses can aid in the early detection and timely intervention of CAD, potentially preventing life-threatening complications like acute coronary syndrome.
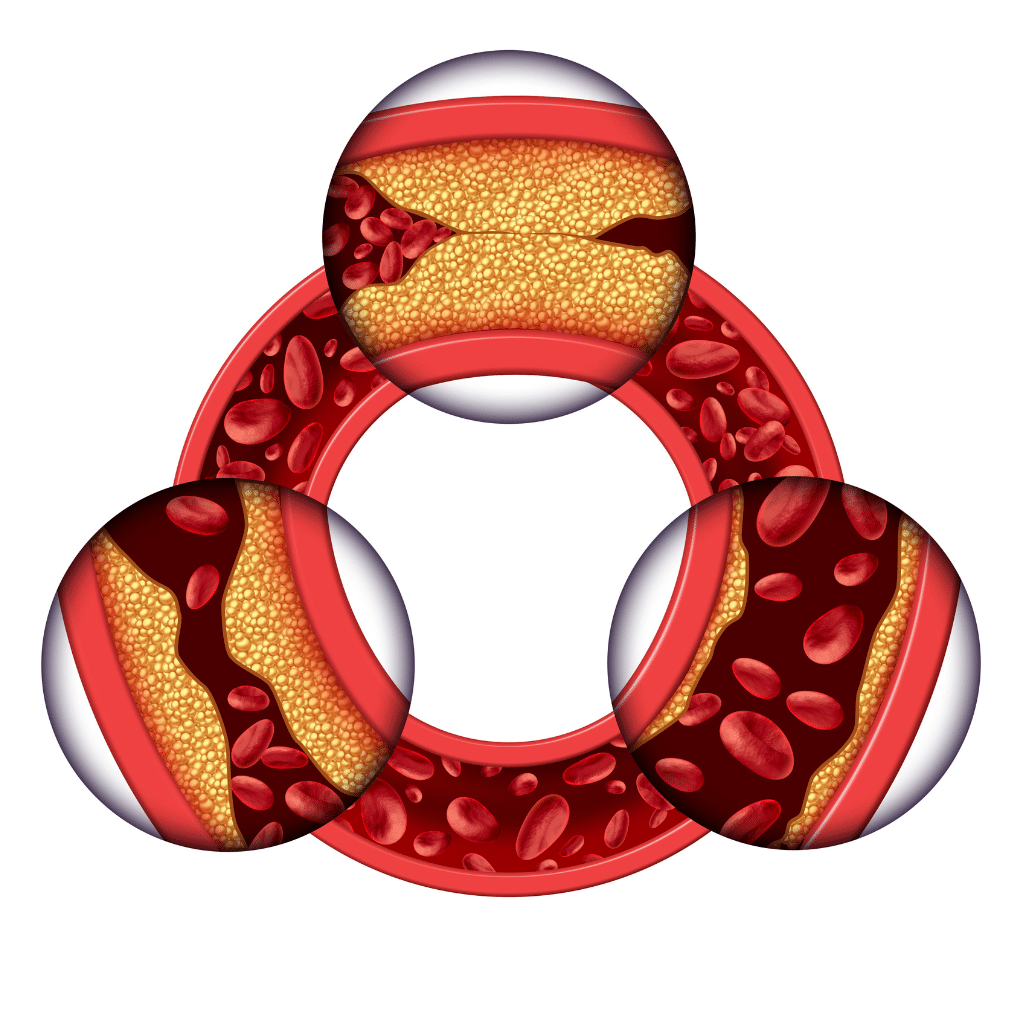
Therapeutic management of CAD involves a combination of medications and procedures aimed at reducing plaque buildup, improving blood flow, and minimizing the risk of clot formation. This includes the administration of cholesterol-lowering medications like statins, anticoagulants to prevent blood clotting, beta blockers to decrease the heart's workload, calcium channel blockers to relax vessels, and nitroglycerin to alleviate chest pain. Additionally, nurses play a critical role in supporting patients undergoing interventions such as angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery. Educating patients on lifestyle modifications, smoking cessation, regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, stress management, and diabetes control is essential to long-term CAD management and prevention. By providing comprehensive care and education, nurses empower patients to take an active role in managing their CAD and reducing the risk of cardiac events.